Brand
Brand is a multi-dimensional term that has generated a profound study to its economic significance and powerful role for a company. The brand concept has been acknowledged for centuries however defining a brand as a notion just started in 1960 by American Marketing Association [8]. A definition of brand was firstly introduced by American Marketing Association (AMA) as “A name, term, design, symbol, or a combination of them, intended to identify the goods or services of one seller or group of sellers and to differentiate them from competitors”. To some extent, brand’s definition from AMA has a narrow scope that only see brand from visible elements such as design, symbol and name. In 1992, Kapferer defined brand into a more holistic view and stated that a brand is beyond a product, it is an essence that has meaning and directions to define its identity. Kapferer has broaden a view about branding and shifted the meaning of brand from only seen as a brand image to a brand identity.
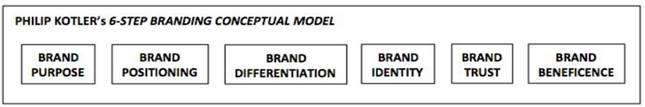
Figure 2: Steps Brand Building by Philip Kotler
Source: (Kotler, 2016)
A decade later, multiple studies have been conducted and provided a wider perspective about the brand. De Chernatony (2006) defined a brand as a dyanamic mean that embedded both functional or emotional benefits for the purpose of creating unique customer’s experiences. Meanwhile, Kotler and Armstrong in 2012, defined a brand as a concept more than just symbols and names, it holds a key relationship between customers and companies because brand accentuates customer’s perceptions and experiences about products/services’ performance. This research will use brand’s definition by De Chernatony in 2006 due to its ability to combine brand-customer relationship with brand’s elements and show the ever-changing situation in branding process.
Brand Building
After a new product has been developed and ready to be launched, it needs to undergo one process called brand building. This research will use Philip Kotler’s brand building model as a theoretical framework due to the comprehensiveness among other models. In the Marketing Journal, Philip Kotler redefined how other companies builds the brand and created 6-step brand building
Brand Purpose
Kotler believes that building a brand should start from a brand purpose. Brand Purpose is a reason for being that simply shows why a brand exists [9]. It functions as a mean to create a better world and as an impact of the brand. Brand purpose is characterized by larger purpose that goes beyond making profit but also giving contribution to the society [9]. Moreover, it represents ethos and clarity that drives a company.
Brand Positioning
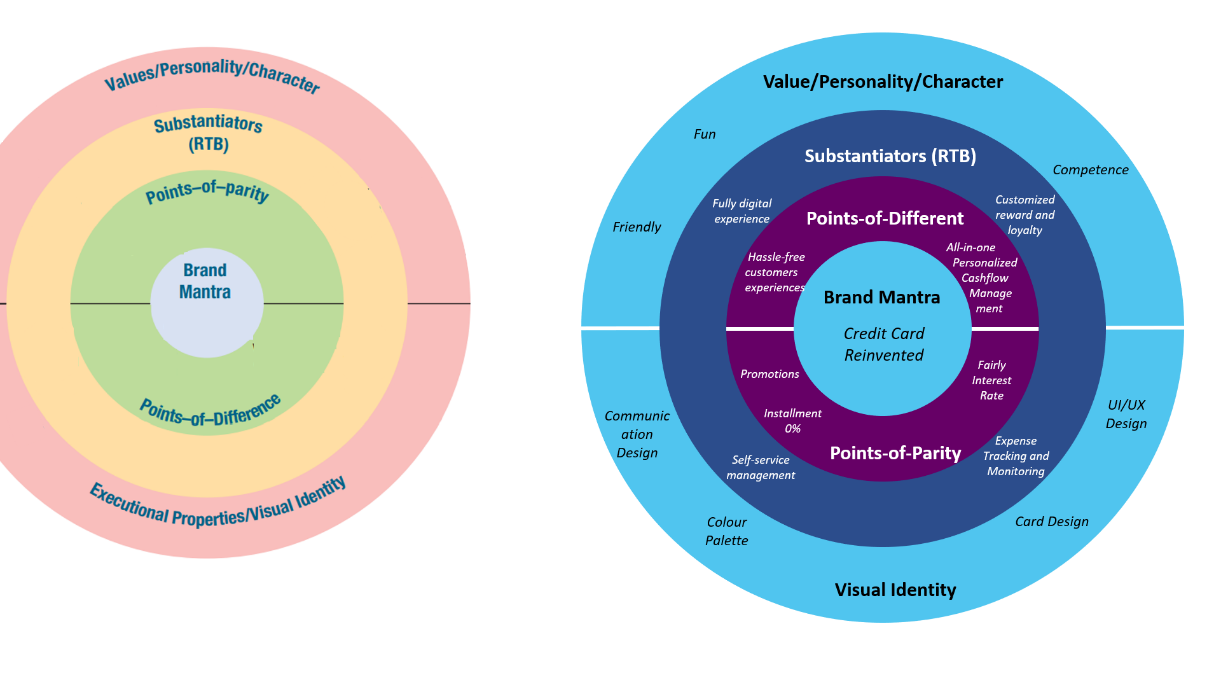
Brand positioning is the second step in Kotler’s brand building conceptual framework. It was defined as all efforts to create a meaningful and distinctive position in the target customer’s mind by designing company’s image and offers. Brand positioning has played pivotal role in overall brand building process. It is aiming to position the brand on top of customers mind by clarifying brand essence, identifying desired customer’s actions and show uniqueness of the brand [19]. It also leads direction of any marketing activities that goes beyond tangible programs such as company’s image and brand intangible [11]. Kotler and Keller introduced a brand positioning bull’s-eye. This tool provides illustration and scheme to visualize and summarize brand positioning strategy. The framework contains of five elements which are:
• Brand mantra
• Point-of-parity (POPs)
• Point-of-difference (PODs)
• Substantiators (Reason-to-believe)
• Personality/Characters, and Visual Identity
First element is brand mantra which is the first step to determine brand positioning. Kotler defines brand mantra as the enunciation of brand’s heart and soul. It acts like other branding concepts such as “brand essence” and “core brand promise” to represent the fundamental aspect of the brand and as a guidance to any marketing activities conducted by internal employees or external partners. Brand mantra builds guidance beyond tactical strategy including how the campaigns run and how the portfolio being managed.
After defining brand mantra, the next step is defining points-of-difference (PODs) and points-of-parity (POPs). Points-of-difference (PODs) refers to unique benefits or attributes associated to a brand that are believed could not be found in other competitors. KFC for example has points of difference as having entirely unique chicken recipe and Starbuck as creating experience beyond drinking coffee. Furthermore, strong brands can have more than 1 point-of-difference such as Apple with ease-of-use, design and irreverent attitude.
The opposite of Point-of-difference (PODs), Points-of-parity (POPs) refers to not necessarily unique benefits or attributes associated to a brand that can be shared with other competitors. Points-of-parity (POPs) is divided into three types which are category, correlational and competitive. Category Points-of-parity (POPs) refers to necessary benefits or attributes that are essentials to be offered in certain product or service category. Points-of-parity (POPs) that aims to attack competitors’ Point-of-difference (PODs) by associating our brand with their PODs attributes.
Third element is Substantiators or reasons-to-believe (RTB). It refer to how brand deliver its desired benefits or attributes. It should accentuate factual or demonstrable support that has been embedded in points-of-difference (PODs) and points-of-parity (POPs).
After substatiators, the next element is personality /character. Kotler and Keller believe that a brand goes beyond functional benefits as a foundation for sustainable and deep customer relationship. Therefore, after defining factual attributes or benefits in previous step, a brand should be embedded with personality as emotional benefits [11]. Kotler and Keller define brand personality as “specific mix of human traits that we can attribute to a particular brand”. The notion of brand personality has been mentioned long before Kotler and Keller. De Chernatony and McDonald have clearly pinpointed that a brand is the personality of a product or service in form of tangible and non-tangible characteristics.
The last step in brand positioning is creating visual identity. Visual identity or executional properties are required to create immediate recognition and awareness in customer’s mind. The difference between visual identity and substantiators (reason-to-believe) is the former emphasizes more tangible aspects that affect directly to the way customers see the brand. Visual identity covers brand’s logo, colour palette, signs, uniforms, building other tangible assets that are associated with a brand.
Brand Differentiation
Kotler and Keller described brand differentiation as a process for the companies to stand out in the way that the competitors cannot match [12]. Many scholars have indicated that brand differentiation has played a major role of brand strategy. Sharp and Dawes furthermore illustrated that a company should be perceived different to outperform in a highly competitive market. It shows the importance of brand differentiations can create significant competitive advantage for the company. Furthermore, companies can achieve a sustainable competitive advantage when they outperform in its market or among competitors for over a prolonged period [13].
Brands with strong differentiation might result in greater profitability for the companies [14]. Differentiated brands have indicated more customer’s loyalty who are less price. This statement was strengthened by Kotler and Keller who describes differentiated brand with the increase of ability to offer premium or higher price. Therefore, those have stronger positions than their competitors that implemented cost leadership strategy. To some extent, the impact of strong brand differentiation is key factors for the brand growth because it can focus on delivering brand quality rather than cost. From the point of view of customers, they find it hard to substitute the brands with other alternatives and affect to the ability to maintain market share.
Brand Identity
Brand identity was chosen Kotler as a fourth step in brandbuilding process. There is an immense definition of brand identity from the scholars. David Aaker in 1996 defines brand identity as “a unique set of brand associations that the brand strategists aspire to create or maintain. It represents what the brand stands for and shows a promise to the customer [15]. This definition has brought to a broader concept of brand identity that, according to him, will enrich the understanding of brand identity by providing insights into what can and cannot be included as brand identity [16]. Similar understanding about brand identity has been brought by Kapferer who described brand identity as a vision that enables innovations, loyalty and advocation driven by core values and key beliefs of the brand [17].
Among all brand identity frameworks, Brand Identity Model by David Aaker provided the most exhaustive approach in planning the brand identity. Therefore, this research will use Aaker framework as a basis for brand identity planning. Aaker’s Brand Identity System consists of four different perspectives that have twelve brand elements in total. Each perspective embodies multi-layered and complex situations that could enhance the process of brand identity planning [16]. In this research, there are three elements that are relevant to the case which are brand as a product, organization and symbol.
Brand as a product is an important perspective of brand identity, as it is directly linked to the user experience and customer’s brand choice. One of the elements is product attribute. This element is about how the product provides functional benefits or sometimes emotional benefits for customers during the use of product or consideration during purchasing process [16]. Therefore, in this element, a company usually offer a value proposition to give something extra or unique that the other competitors lack or even don’t have.
Brand as an organization is seen as a more resistant and endurable strategy compare to product attributes above. When a brand is associated with an organization, it will be harder to be duplicated by other competitors [16]. At the same time, organizational attributes are hard to evaluate that make even more difficult for competitors to narrow the gap. Some brands are part of an organization that are associated with certain attributes. Those association could affect the way a brand is perceived by customers.
Brand as a person can become a foundation to build relationship with the customers as it has personality to be connected with. A study from Keller and Lehman has discovered personal component of relationship between a brand and its customers [18]. The study mentioned Fournier’s view on six dimensions of customer-brand relationship which are self-concept connection, commitment or nostalgic attachment, behavioral interdependence, love/passion, intimacy, and brand partner quality. Fournier moreover categorized typology of customer-brand relationships which are arranged marriages, casual friends/buddies, marriages of convenience, committed partnerships, best friendships, compartmentalized friendships, kinships, rebounds/avoidance-driven relationships, childhood friendships, courtships, dependencies, flings, enmities, secret affairs, and enslavements.
Brand Trust
Kotler defined brand trust as ability of a brand to deliver their promises to customers [19]. Meanwhile, Chaudhuri and Holbrook defined Brand Trust as willingness of overage customers to have confidence in the brand’s function to perform. Brand trustis aiming to form the feeling of security from customers and build up long term relationship with customers. Recently, a study conducted by Anna Simonova shows that brand trust has substantial impact in increasing customer’s commitment, satisfaction and brand loyalty in which will have significant impact in increasing company’s value such as low level of entry barriers from newcomers, less-sensitive price customers, and revenue increased. Therefore, brand trust is something to be accomplished by any brands.
Brand Beneficence
After earning a sustain trust from the customers, the final step is focus on demonstrating a brand beneficence. Brand beneficence refers to the context when the brand offers benefits and minimize negative impact to individuals or society at large [5]. Moreover, Kotler has emphasized that brand beneficence is the best way set a brand apart from other competitors by showing brand’s ability to serve both individual and society as a whole. This can be illustrated on Brand Marlboro as an example. As one of most popular cigarette’s brands, it might deliver high customer satisfaction with its enjoyable taste. However, it can damage people’s health by some diseases associated with smoking. In the end, Marlboro doesn’t benefit either customers or surrounding people [5].
Although a company has flexibility to determine its brand beneficence, it should consider whether the brand has beneficence problems or whether it creates potential negative impact to the brand [5]. For instance, food and beverage companies that offers junk food with high sugar level, salt and other ingredients leading to certain illness has facing a decline trend due to the shifting of customer’s behaviour into a healthier lifestyle.
Marketing
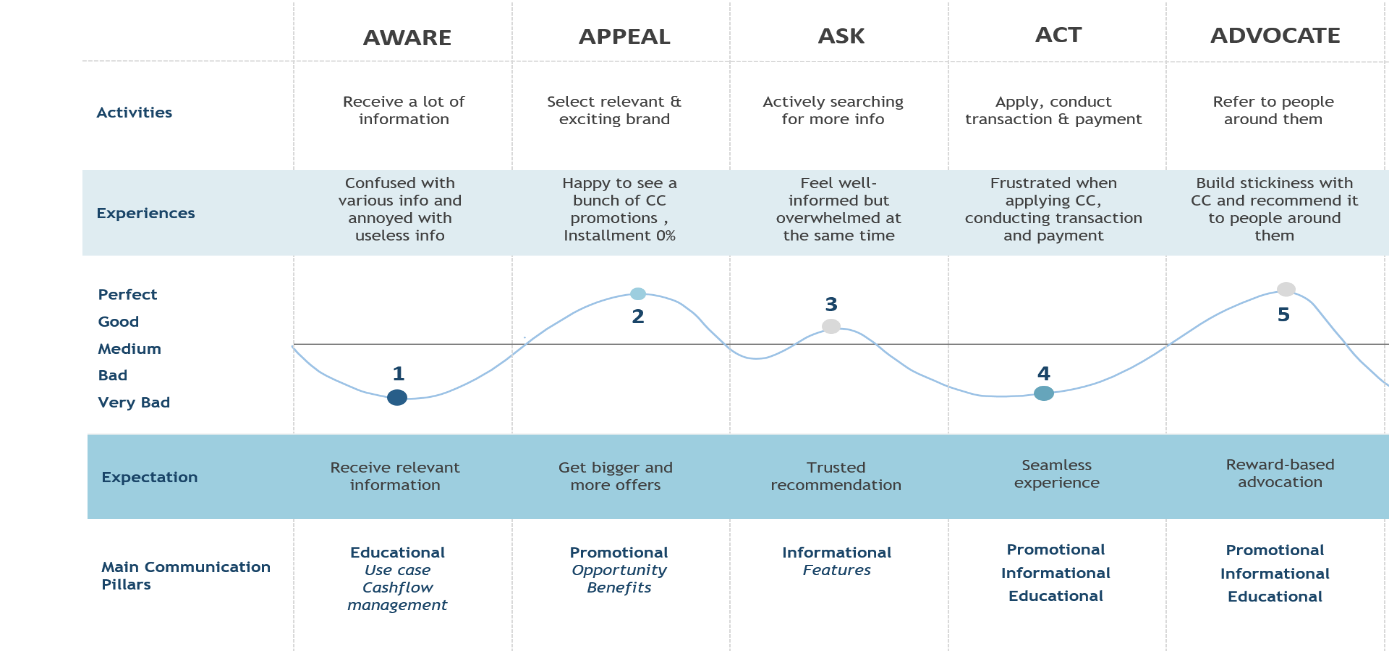
The concept of customer path was introduced in 1989 by E. St. Elmo Lewis through the concept of AIDA as an abbreviation for Attention, Interest, Desire and Action [20]. Long after that, Derek Rucker modified AIDA into four A’s that consists of Aware, Attitude, Act and Act again [21]. This modification has brought a post-purchase analysis that brand loyalty has become important element and was driven by repurchase actions. However, in 2017, Philip Kotler [21], Hermawan Kartjaya, and Iwan Setiawan refined the four A’s concept to become five A’s [21]. Driven by shifting into a fully connected world, they argued that a straightforward funnel such as four A’s needs to be revised. Therefore, Philip Kotler, Hermawan Kartjaya, and Iwan Setiawan have rewritten the four A’s concept as the five A’s: Aware, Appeal, Ask, Act, and Advocate.
Awareness is an initial stage to entire customer path. In the era where massive information has been exposed to the customers, they experience strong influence from people around them and variety of marketing communications. This stage is crucial as a getaway for customers to recall and recognize the brand that strongly driven by marketing channels and word of mouth by other customers.
Second stage is appeal that was characterized by a process of creating short-term memory or even amplifying long-term memory of some brands that have “wow factors”. This stage happened after customers have awareness to some brands by being exposed to any means of communications or become attracted only to a few couple of brands. Appealing stage has become more challenging in current business landscape where competition is fiercer than ever. Furthermore, in order to win among abundant of products and services, companies should presence a strong brand appeal. This stage is specifically more crucial for younger segment due their potentials to be early adopters of new product and services. However, the ultimate objective of this stage is to trigger customer’s curiosity and “force” them to move to the next stage.
The ask stage is prompted by customers curiosity that happened in previous stage to actively researching for more information about the brands they are attracted to. In the connected world, there are numberless channels ranging from media, people around them to the brand itself. Customers can directly ask for advice from some friends or family, they might call contact centers or search the online product reviews. In the era where everything is fully connected, building only digital presence is not enough. There should be an integration between offline and online channels in order to create a seamless experience for customers. In this stage, customer’s path shifts from individual to social in which customer’s outer world makes strong influence to their decisions. Therefore, in this stage, it is crucial to build a presence in the most popular channels.
After being convinced in the ask stage, customers will conduct some actions in act stage. The time customers spend to buying process can be various depends on the perceive importance of the products or services. The customers actions in this stage are not limit to only buying process, but further into post-buying actions. Therefore, the brands should create customers engagement and shaping a whole positive experience. The engaged customers will not only reinforce purchasing actions but also stickiness and total ownership to the brand. These elements are essentials to bring customers to the next stage.
The last stage is advocate that was triggered by customer’s strong brand loyalty that makes them to recommend the brands without being asked to. In the era where tons of information are inevitable, recommendations from surrounding people has played vital role in customer’s decisions. Unfortunately, not all loyal customers are actively advocating the brands to others. Therefore, companies should encounter some catalysts that could enforce a situation when customers feel obliged to recommend the brands.